Active_Directory_trust_setup#
Description#
This page explains how to setup and configure cross-forest trust between an IPA domain and an AD (Active Directory) domain.
Prerequisites#
FreeIPA 3.3.3 or later is recommended
Windows Server 2008 R2 or later with configured AD DC and DNS installed locally on the DC
IPv6 stack usage#
Recommended way for contemporary networking applications is to only open IPv6 sockets for listening because IPv4 and IPv6 share the same port range locally. FreeIPA uses Samba as part of its Active Directory integration and Samba requires enabled IPv6 stack on the machine.
Adding ipv6.disable=1 to the kernel command line disables the
whole IPv6 stack
Adding ipv6.disable_ipv6=1 will keep the IPv6 stack functional
but will not assign IPv6 addresses to any of your network devices. This
is recommended approach for cases when you don’t use IPv6 networking.
Creating and adding to for example /etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.conf will avoid assigning IPv6 addresses to a specific network interface
# Disable IPv6
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.``\ ``.disable_ipv6 = 1
where interface0 is your specialized interface.
Note that all we are requiring is that IPv6 stack is enabled at the kernel level and this is recommended way to develop networking applications for a long time already.
Trusts and Windows Server 2003 R2#
As noted above, the requirement for trusts is Windows Server 2008 R2. While cross-forest trusts were added to forest functional level Windows Server 2003, there are additional requirements imposed by use of AES encryption types which require domain functional level Windows Server 2008. It is possible to establish a trust between a FreeIPA server and Windows Server 2003 R2, with limited functionality with only RC4 and DES encryption types. Next paragraph describes the actions needed in order to do this. Please note, however, that this is unsupported, highly experimental and of very limited value because of the weak encryption types for trusted domain objects which can be reasonably easy cracked with current advances in technology.
In order to establish a trust between a FreeIPA server and a Windows Server 2003 R2, you need to raise the forest functional level to Windows Server 2003. To do this, open ‘Active Directory Domains and Trusts’ snap-in and right-click on ‘Active Directory Domains and Trusts’ root in the left pane. Then select ‘Raise forest functional level …’ and use ‘Windows Server 2003’ as the level to raise.
Make sure you perform this action before establishing a trust with the ‘ipa trust-add’ command. The rest of the setup is identical to that of Windows Server 2008 R2.
Assumptions#
IPA server IP address: ipa_ip_address (e.g. 10.16.78.61)
IPA server hostname: ipa_hostname (e.g. ipaserver.ipadomain.example.com)
IPA domain: ipa_domain (e.g. ipadomain.example.com)
IPA NetBIOS: ipa_netbios (e.g. IPADOMAIN)
IPA Kerberos realm, IPA_DOMAIN, is equal to IPA domain (e.g. IPADOMAIN.EXAMPLE.COM and ipadomain.example.com)
AD DC IP address: ad_ip_address (e.g. 10.16.79.150)
AD DC hostname: ad_hostname (e.g. adserver)
AD domain: ad_domain (e.g. addomain.example.com)
AD NetBIOS: ad_netbios (e.g. ADDOMAIN)
AD admins group SID: ad_admins_sid (e.g. S-1-5-21-16904141-148189700-2149043814-512)
NOTE: AD domain and IPA domain must be different, this is very basic requirement for any Active Directory cross-forest trust.
NOTE: italicized text should be replaced with real values. E.g. if
IPA domain is ipadomain.example.com, and the IP address of IPA
server is 10.16.78.61, the command:
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /ZoneAdd ipa_domain /Forwarder ipa_ip_address
should look like this:
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /ZoneAdd ipadomain.example.com /Forwarder 10.16.78.61
NOTE: NetBIOS name is the leading component of the domain name. E.g.
if the domain name is ipadomain.example.com, the NetBIOS name is
IPADOMAIN. NetBIOS namespace is flat, there should be no conflicts
between all NetBIOS names. NetBIOS names of the IPA domain and AD domain
must be different. In addtion, NetBIOS names of the IPA server and AD DC
server must be different.
Install and configure IPA server#
Make sure all packages are up to date#
# yum update -y
Install required packages#
# yum install -y "*ipa-server" "*ipa-server-trust-ad" bind bind-dyndb-ldap
Configure host name#
# hostnamectl set-hostname ipa_hostname
Install IPA server#
# ipa-server-install -a mypassword1 -p mypassword2 --domain=ipa_domain --realm=IPA_DOMAIN --setup-dns --no-forwarders -U
Login as admin#
To obtain a ticket-granting ticket, run the follwing command:
# kinit admin
The password is your admin user’s password (from -a option in the
ipa-server-install comand).
Make sure IPA users are available to the system services#
# id admin
# getent passwd admin
Both above commands should return information about the admin user. If
above commands fail, restart the sssd service
(service sssd restart), and try them again.
Configure IPA server for cross-forest trusts#
# ipa-adtrust-install --netbios-name=ipa_netbios -a mypassword1
When planning access of AD users to IPA clients, make sure to run ipa-adtrust-install on every IPA master these IPA clients will be connecting to.
Cross-forest trust checklist#
Before establishing a cross-forest trust, some additional configuration must be performed.
Date/time settings#
Make sure both timezone settings and date/time settings on both servers match.
Firewall configuration#
On AD DC#
Windows Firewall configuration (to be added).
On IPA server#
IPA uses the following ports to communicate with its services:
TCP ports: 80, 88, 443, 389, 636, 88, 464, 53, 135, 138, 139, 445, 1024-1300
UDP ports: 88, 464, 53, 123, 138, 139, 389, 445
These ports must be open and available; they cannot be in use by another service or blocked by a firewall. Especially ports 88/udp, 88/tcp, 389/udp are important to keep open on IPA servers to allow AD clients to obtain cross-realm ticket granting tickets or otherwise single sign-on between AD clients and IPA services will not work.
Ports 135, 1024-1300 are needed to get DCE RPC end-point mapper to work. End-point mapper is a key component to accessLSA and SAMR pipes which are used to establish trust and access authentication and identity information in Active Directory.
Previously we recommended that you should make sure that IPA LDAP server is not reachable by AD DC by closing down TCP ports 389 and 636 for AD DC. Our current tests lead to the assumption that this is not necessary anymore. During the early development stage we tried to create a trust between IPA and AD with both IPA and AD tools. It turned out that the AD tools expect an AD like LDAP schema and layout to create a trust. Since the IPA LDAP server does not meet those requirements it is not possible to create a trust between IPA and AD with AD tools only with the ‘ipa trust-add’ command. By blocking the LDAP ports for the AD DC we tried to force the AD tools to fall back to other means to get the needed information with no success. But we kept the recommendation to block those ports because it was not clear at this time if AD will check the LDAP layout of a trust partner during normal operation as well. Since we have not observed those request the recommendation can be dropped.
Below are instructions on how to configure the firewall using
iptables.
Firewalld#
Fedora 18 introduced a new firewall manager: firewalld. However,
firewalld does not yet support allowing and blocking services for
specific hosts. For this reason, we recommend disabling firewalld,
enabling iptables and using the sample configuration listed in
section #iptables.
To disable firewalld:
# chkconfig firewalld off
# service firewalld stop
To enable iptables:
# yum install -y iptables-services
# chkconfig iptables on
Make sure iptables configuration file is located at
/etc/sysconfig/iptables and contains the desired configuration, and
then (re)start the iptables service:
# service iptables restart
iptables#
Make sure that iptables is configured to start whenever the system
is booted:
# chkconfig iptables on
iptables configuration file is /etc/sysconfig/iptables. Taking
into account the rules that must be applied in order for IPA to work
properly, here is a sample configuration.
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
# -A INPUT -s ad_ip_address -p tcp -m multiport --dports 389,636 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j REJECT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,88,443,389,636,88,464,53,138,139,445 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p udp -m multiport --dports 88,464,53,123,138,139,389,445 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p udp -j REJECT
-A INPUT -p tcp -j REJECT
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
Please note that the line containing “ad_ip_address” is not needed anymore (see comments above). If you still want to use it please make sure you replace ad_ip_address in the above configuration, with the IP address of AD DC.
Any changes to the iptables configuration file will require a
restart of the iptables service:
# service iptables restart
DNS configuration#
NOTE: Any changes to /etc/resolv.conf file will require a
restart of krb5kdc, sssd and httpd services.
Both AD and IPA domains need to be visible to each other. In normal DNS configuration, no changes are required. When the testing DNS domains are not part of shared DNS tree visible to both IPA and AD, customer DNS zone forwarders can be created:
Conditional DNS forwarders#
On AD DC, add conditional forwarder for IPA domain:
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /ZoneAdd ipa_domain /Forwarder ipa_ip_address
On IPA server, add conditional forwarder for AD domain. The command in IPA version 3 and 4 are different.
IPA v3.x:
# ipa dnszone-add ad_domain –name-server=ad_hostname.ad_domain –admin-email=’hostmaster@ad_domain’ –force –forwarder=ad_ip_address –forward-policy=only –ip-address=ad_ip_address
IPA v4.x:
# ipa dnsforwardzone-add ad_domain --forwarder=ad_ip_address --forward-policy=only
If AD is subdomain of IPA#
If the AD domain is a subdomain of the IPA domain (e.g. AD domain is
addomain.ipadomain.example.com and IPA domain is
ipadomain.example.com), configure DNS as follows.
On IPA server, add an A record and a NS record for the AD domain:
# ipa dnsrecord-add ipa_domain ad_hostname.ad_netbios --a-ip-address=ad_ip_address``
# ipa dnsrecord-add ipa_domain ad_netbios --ns-hostname=ad_hostname.ad_netbios``
On AD DC, there two options.
The first one is to configure a global forwarder to forward DNS queries to the IPA domain:
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /ResetForwarders ipa_ip_address /Slave
The second option is to configure a DNS zone for master-slave replication. The data for this zone will then be periodically copied from master (IPA server) to slave (AD server).
To do this, first explicitly allow the transfer of the zone on IPA server:
# ipa dnszone-mod ipa_domain --allow-transfer=ad_ip_address
And second, add the DNS zone for the IPA domain on the AD DC:
C:\> dnscmd 127 0.0.1 /ZoneAdd ipa_domain /Secondary ipa_ip_address
If IPA is subdomain of AD#
If the IPA domain is a subdomain of the AD domain (e.g. IPA domain is ipadomain.addomain.example.com and AD domain is addomain.example.com), configure DNS as follows.
On AD DC, add an A record and a NS record for the IPA domain:
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /RecordAdd ad_domain ipa_hostname.ipa_domain A ipa_ip_address
C:\> dnscmd 127.0.0.1 /RecordAdd ad_domain ipa_domain NS ipa_hostname.ipa_domain
Verify DNS configuration#
To make sure both AD and IPA servers can see each other, check if SRV records are being properly resolved.
On AD DC:
C:\> nslookup
> set type=srv
> _ldap._tcp.ad_domain``
> _ldap._tcp.ipa_domain``
> quit
On IPA server:
# dig SRV _ldap._tcp.ipa_domain``
# dig SRV _ldap._tcp.ad_domain``
Establish and verify cross-forest trust#
Add trust with AD domain#
When AD administrator credentials are available#
# ipa trust-add --type=ad ad_domain --admin Administrator --password
Enter the Administrator’s password when prompted. If everything was set up correctly, a trust with AD domain will be established.
The user account used when creating a trust (the argument to the
--admin option in the ipa trust-add command) must be a member of
the Domain Admins group.
At this point IPA will create one-way forest trust on IPA side, will
create one-way forest trust on AD side, and initiate validation of the
trust from AD side. For two-way trust one needs to add
--two-way=true option.
Note that there is currently an issue in creating a one-way trust to Active Directory with a shared secret instead of using administrative credentials. This is due to lack of privileges to kick off a trust validation from AD side in such situation. The issue is being tracked in this bug.
The ipa trust-add command uses the following method calls on the AD
server:
`CreateTrustedDomainEx2<http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc234380.aspx>`__ to create the trust between the two domains`QueryTrustedDomainInfoByName<http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc234376.aspx>`__ to check if the trust is already added`SetInformationTrustedDomain<http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc234385.aspx>`__ to tell the AD server that the IPA server can handle AES encryption
When AD administrator credentials aren’t available#
# ipa trust-add --type=ad "ad_domain" --trust-secret
Enter the trust shared secret when prompted. At this point IPA will create two-way forest trust on IPA side. Second leg of the trust need to be created manually and validated on AD side. Following GIF sequence shows how trust with shared secret is created:
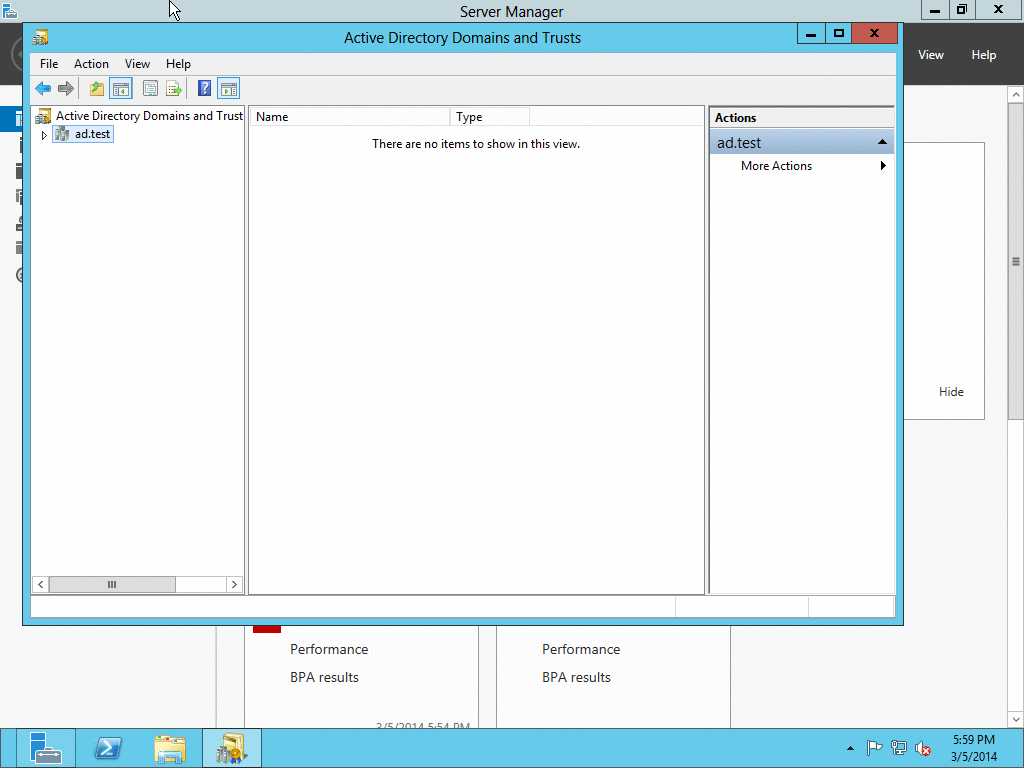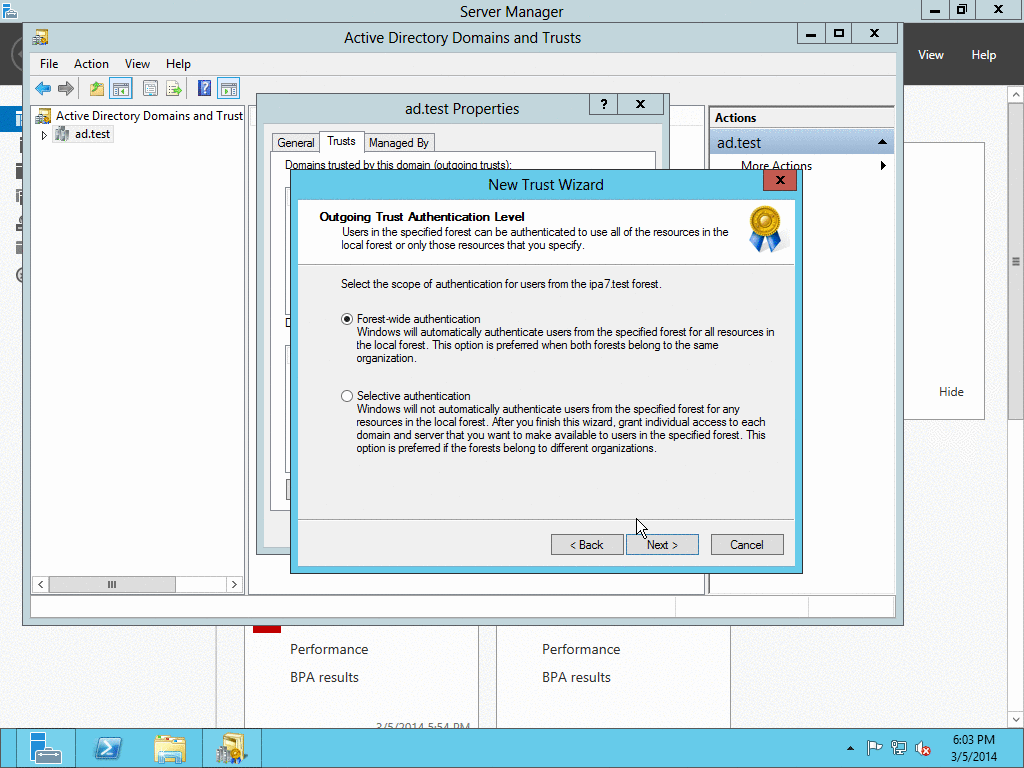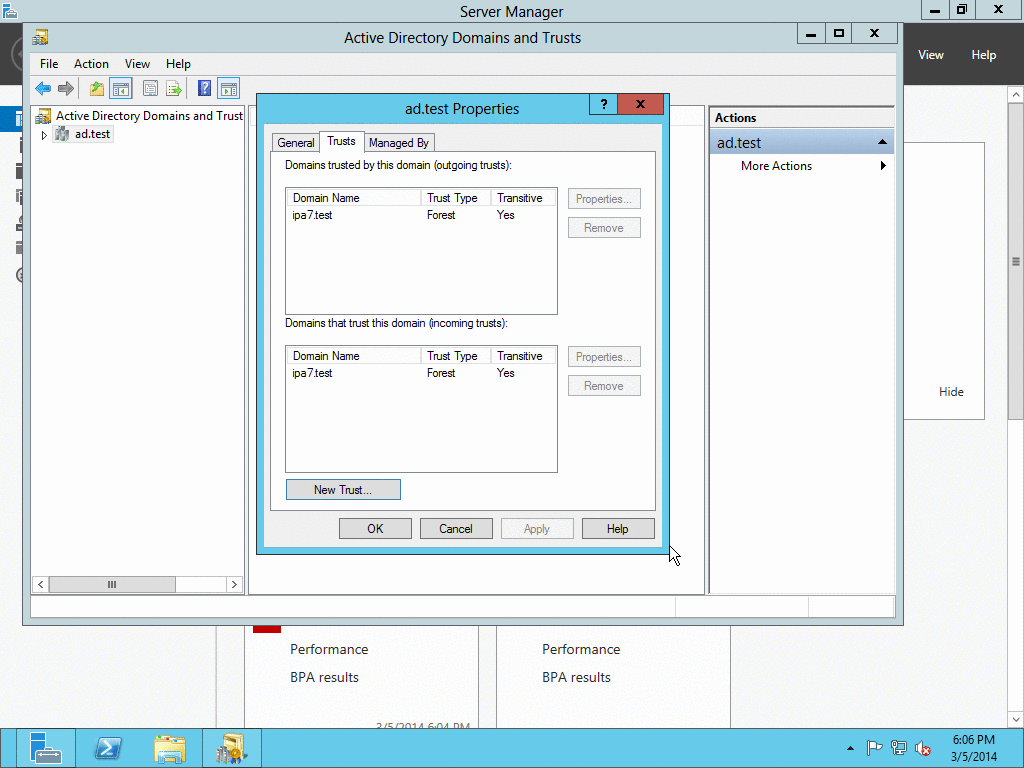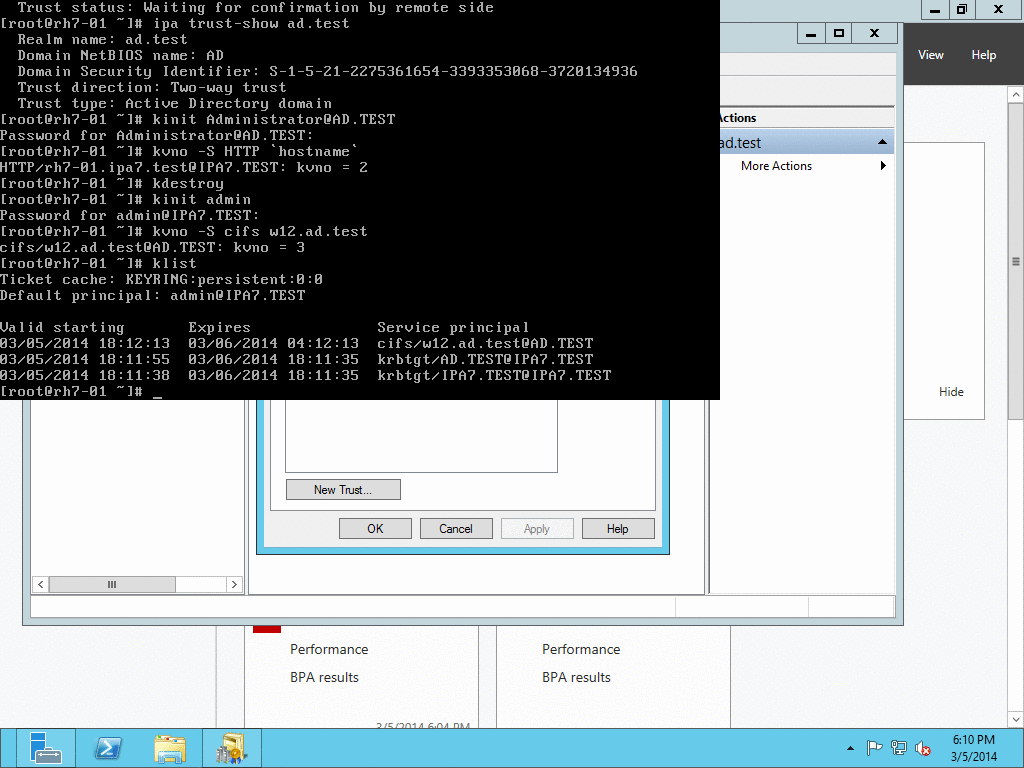
Trust-ad-demo-shared-secret.gif#
Once trust leg on AD side is established, one needs to retrieve the list of trusted forest domains from AD side. This is done using following command:
# ipa trust-fetch-domains "ad_domain"
With this command running successfuly, IPA will get information about trusted domains and will create all needed identity ranges for them.
Use “trustdomain-find” to see list of the trusted domains from a trusted forest:
# ipa trustdomain-find "ad_domain"
Edit /etc/krb5.conf#
Many applications ask Kerberos library to verify that Kerberos principal can be mapped to some POSIX account. Additionally, there are some applications that perform additional check by asking the OS for the canonical name of the POSIX account returned by Kerberos library. Note that OpenSSH compares the name of principal unchanged but SSSD low-cases the realm part, thus real user name is Administrator@realm, not administrator@realm, when trying to logon with Kerberos ticket over SSH.
We have several factors in play here:
Kerberos principals use form name@REALM where REALM has to be upper case in Linux
SSSD provides POSIX accounts to AD users always fully qualified (name@domain)
SSSD normalizes all POSIX accounts to lower case (name@domain) on requests which involve returning POSIX account names.
Thus, we need to define rules for mapping Kerberos principals to system user names. If MIT Kerberos 1.12+ is in use and SSSD 1.12.1+ is in use, you can skip the rest of this section because they implement a localauth plugin that automatically does this translation and is set up by ipa-client-install.
If no SSSD support for localauth plugin is available, we need to specify auth_to_local rules that map REALM to a low-cased version. auth_to_local rules are needed to map a successfully authenticated Kerberos principal to some existing POSIX account.
For the time being, a manual configuration of /etc/krb5.conf on the
IPA server is needed, to allow Kerberos authentication.
Add these two lines to /etc/krb5.conf on every machine that is going
to see AD users:
[realms]
IPA_DOMAIN = {
....
auth_to_local = RULE:[1:$1@$0](^.*@AD_DOMAIN$)s/@AD_DOMAIN/@ad_domain/
auth_to_local = DEFAULT
}
Restart KDC and sssd
# service krb5kdc restart
# service sssd restart
Allow access for users from AD domain to protected resources#
Before users from trusted domain can access protected resources in the IPA realm, they have to be explicitly mapped to the IPA groups. The mapping is performed in two steps:
Add users and groups from trusted domain to an external group in IPA. External group serves as a container to reference trusted domain users and groups by their security identifiers
Map external group to an existing POSIX group in IPA. This POSIX group will be assigned proper group id (gid) that will be used as default group for all incoming trusted domain users mapped to this group
Create external and POSIX groups for trusted domain users#
Create external group in IPA for trusted domain admins:
# ipa group-add --desc='ad_domain admins external map' ad_admins_external --external
Create POSIX group for external ad_admins_external group:
# ipa group-add --desc='ad_domain admins' ad_admins
Add trusted domain users to the external group#
# ipa group-add-member ad_admins_external --external 'ad_netbios\Domain Admins'
When asked for member user and member group, just leave it blank and hit Enter.
NOTE: Since arguments in above command contain backslashes, whitespace, etc, make sure to either use non-interpolation quotes (’) or to escape any specials characters with a backslash ().
Add external group to POSIX group#
Allow members of ad_admins_external group to be associated with
ad_admins POSIX group:
# ipa group-add-member ad_admins --groups ad_admins_external
Test cross-forest trust#
Using SSH#
AD users should now be able to login into IPA domain via SSH. putty SSH client for Windows (http://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe) can be used to test this. When trying to connect to the IPA domain, make sure you use ad_user@ad_domain as username. Note that ad_domain must be lower-case. Also, make sure you preserve the case of the username, i.e. if username is Administrator, log in as Administrator@ad_domain, not administrator@ad_domain.
Using Kerberized web applications#
If you need to install and configure a web application for the purposes of testing Kerberos authentication, MediaWiki can be used.
To add Kerberos authentication to an existing web application, the following Apache configuration is needed:
<Location "/mywebapp">
AuthType Kerberos
AuthName "IPA Kerberos authentication"
KrbMethodNegotiate on
KrbMethodK5Passwd on
KrbServiceName HTTP
KrbAuthRealms IPA_DOMAIN
Krb5Keytab /etc/httpd/conf/ipa.keytab
KrbSaveCredentials off
Require valid-user
Make sure you replace IPA_DOMAIN in the above configuration with your actual IPA domain (in caps) and to restart the apache service:
# service httpd restart
Debugging trust#
General debugging guidelines#
What you can do is following (assumes Fedora 20+ or RHEL 7+):
Check that IPv6 module is not disabled on the Linux side as Samba and CLDAP module in IPA require it. See instructions above.
Check firewall rules: AD DCs should be able to contact IdM smbd over 138/139/445 TCP and UDP ports, 389 UDP port.
Stop smb and winbind services on IdM server
`` systemctl stop smb winbind``
Set log level to increased debug so that packets smbd/winbindd receive get printed fully in the logs:
`` net conf setparm global ‘log level’ 100``
Set log level to increased debug so that communication done by IPA when establishing trust is printed fully in the logs. Change /usr/share/ipa/smb.conf.empty:
[global]
log level = 100
Remove old /var/log/samba/log.*
Start smb and winbind services
`` systemctl start smb winbind``
Re-add trust
`` ipa trust-add \ `` ...
If trust-add command was used with shared secret instead of explicit AD administrator credentials, after validation was performed from AD side, run
`` ipa trust-fetch-domains ``
Package following logs and attach them to a bug or send directly to a member of FreeIPA development team who requested the logs. Please do not send logs to the public mailing lists – logs are often quite large and would contain information specific to your AD deployment that general public shouldn’t have access to. The logs we are interested in are following:
/var/log/httpd/error_log
/var/log/samba/log.*
Failures due to exhausted DNA range on replica#
It may happen that the trust-add command fails with the generic
ipa: ERROR: communication with CIFS server was unsuccessful message
displayed in the console and Apache error log containing the following
message:
<SNIP>
s4_tevent: Run immediate event "tstream_smbXcli_np_readv_trans_next": 0x7f6e603b7f60
s4_tevent: Schedule immediate event "tevent_req_trigger": 0x7f6e603b6be0
s4_tevent: Run immediate event "tevent_req_trigger": 0x7f6e603b6be0
s4_tevent: Destroying timer event 0x7f6e6038db50 "dcerpc_timeout_handler"
s4_tevent: Schedule immediate event "tevent_req_trigger": 0x7f6e603b7d20
s4_tevent: Run immediate event "tevent_req_trigger": 0x7f6e603b7d20
lsa_CreateTrustedDomainEx2: struct lsa_CreateTrustedDomainEx2
out: struct lsa_CreateTrustedDomainEx2
trustdom_handle : *
trustdom_handle: struct policy_handle
handle_type : 0x00000000 (0)
uuid : 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
result : NT_STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL
rpc reply data:
[0000] 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........ ........
[0010] 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 C0 ........
[Thu Dec 01 11:23:21.424668 2016] [wsgi:error] [pid 50403] ipa: INFO: [jsonserver_session] admin@IPA.REALM: trust_add/1(u'ad.realm', realm_admin=u'Administrator', realm_passwd=u'********', bidirectional=True, version=u'2.215'): RemoteRetrieveError
This error may be caused by exhaustion of DNA range on replica caused e.g. by hastily decommissioning malfunctioning master without transferring remaining posix ID ranges to replicas. During trust setup Trusted Domain Object with allocated UID/GID must be created on FreeIPA server. Since UID/GID allocation fails, the whole trust creation process ends with error.
You may search for dnaRemainingValues attribute in
cn=posix-ids,cn=dna,cn=ipa,cn=etc,$SUFFIX subtree to confirm this:
# ldapsearch -Y EXTERNAL -H 'ldapi://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fslapd-IPA-REALM.socket' -b 'cn=posix-ids,cn=dna,cn=ipa,cn=etc,dc=ipa,dc=realm' '(objectClass=dnaSharedConfig)' dnaRemainingValues
SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
# extended LDIF
#
# LDAPv3
# base <cn=posix-ids,cn=dna,cn=ipa,cn=etc,dc=dom-204,dc=ipa,dc=realm> with scope subtree
# filter: (objectClass=dnaSharedConfig)
# requesting: dnaRemainingValues
#
# replica.ipa.realm + 389, posix-ids, dna, ipa, etc, ipa.realm
dn: dnaHostname=replica.ipa.realm+dnaPortNum=389,cn=posix-
ids,cn=dna,cn=ipa,cn=etc,dc=ipa,dc=realm
dnaRemainingValues: 0 <-- no UIDs/GIDs left
# search result
search: 2
result: 0 Success
# numResponses: 2
# numEntries: 1
If this is the case, then follow this guide to re-create POSIX ranges on the replica. Then try to re-establish trust; it should complete successfuly now.
