NTP_Servers_Configuration#
Overview#
Currently the configuration and synchronization of the NTP service is integrated into the FreeIPA system, so supporting a new time server or changing/debugging the old one turns is inconvenient and time-consuming. Besides, FreeIPA currently supports only one ntp service, it’s chrony. Yes, chrony is a modern and secure time server, but not all distributions work with chrony like Fedora 28. However, many Linux distributions are using the FreeIPA system, so they need to support the new version.
Use Cases#
The proposed solution is to make the ntp module independent, not integrated into the FreeIPA system, and make it support three different time servers (chrony, ntpd, openntpd). This increases the FreeIPA system’s flexibility in respect of adding support for new time servers and re-configuring old ones. Also, other distributions, which supported other ntp services, will be able to get a fresh version of the IPA system.
Design#
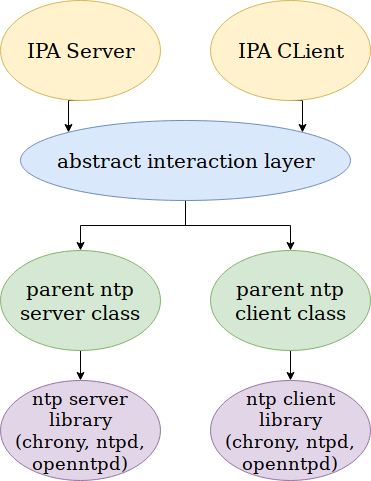 At the time synchronization stage, when the ipa
server/client is being installed or when the state is being restored, a
request is sent to the abstract layer which defines the type of the ntp
service installed in the system. This is done by a package manager. The
type of the package manager is defined by the type of the supported
distribution (Fedora rpm, Debian deb).
At the time synchronization stage, when the ipa
server/client is being installed or when the state is being restored, a
request is sent to the abstract layer which defines the type of the ntp
service installed in the system. This is done by a package manager. The
type of the package manager is defined by the type of the supported
distribution (Fedora rpm, Debian deb).
When the type of the ntp service is defined, its class, inherited from the parent class, is being created (the lower level of the scheme). All ntp classes work on the basis of the parent class. It contains methods of configuration, synchronization and initial state restore. The lower level ntp classes just redefine some of the parent class variables, the values of which depend on the specific type of the ntp service. After that the required ntp method is called (configuration, synchronization, state restore). If the time synchronization is successful, a dns record of the ntp server will be added.
All supported ntp services support the “server” and “pool” options, values of which are written to fields specific to each ntp service when the synchronization is being configured.
When the ntp service is being configured and synchronized, its initial state and the state of its configuration file are saved; when the ipa server/client is deleted, the initial state of the ntp service and its configuration are restored.
All actions related to configuration and synchronization of the ntp service are performed automatically; the user just needs to install a preferred ntp daemon in the system.
Implementation#
The abstract layer is represented by the ipalib/createntp.py module, with which the ipa server/client directly communicates at the time synchronization stage. Once the type of the ntp service is defined, the specific ntp class is created according to the type. The ntp class is generated from ipaserver/install/servntplib.py and ipaclient/install/clintplib.py (for the server and for the client, accordingly). The created ntp class is inherited from the parent class ipaserver/install/servntpconf.py or ipaclient/install/clintpconf.py.
During the FreeIPA installation, an additional package containing modules for the ntp service configuration and time synchronization is installed: python-ipaserver-ntplib and python-ipaclient-ntplib (for the client and for the server, accordingly). Additional ntp packages do not contain dependencies on specific ntp services and their installation will not affect the system environment; it will just enable the FreeIPA to synchronize the time.
The user has to choose whether to install the package with the ipa ntp modules or not. If user installed ipa ntp package, the type of the ntp service is defined during the installation of the ipa server/client. If no supported ntp services are found in the system and the installation is run without the “-N” option, the user will receive a warning and the installation will finish. If the “-N” option is present, all settings and the time synchronization will be ignored.
The priority of choosing the ntp service is the following: chrony, ntpd, openntpd.
CLI
As stated above, you don’t need any other settings and flags in order to select the ntp service; the ntp module detects the time server automatically. You need to have a distribution with an ntp daemon (chrony, ntpd or openntpd) and an appropriate IPA ntp library. But you can use flags to add ntp servers for synchronizing time. Example:
Command |
Options |
Behavior |
|---|---|---|
ipa-server-install |
-N |
will NOT configure and NOT start a local ntp service |
ipa-server-install |
will use ntp service installed in the system and public ntp pool in configuration |
|
ipa-server-install |
–ntp -server=1.ntp.server –ntp -server=2.ntp.server |
will configure ntp service using 1.ntp.server and 2.ntp.server NTP servers |
ipa-server-install |
–ntp-p ool=example.ntp.pool |
will configure ntp service using “example.ntp.pool” NTP pool |
ipa-replica-install |
-N |
will NOT configure and NOT start a local ntp service |
ipa-replica-install |
will use ntp service installed in the system and public ntp pool in configuration |
|
ipa-replica-install |
–ntp -server=1.ntp.server –ntp -server=2.ntp.server |
will configure ntp service using 1.ntp.server and 2.ntp.server NTP servers |
ipa-replica-install |
–ntp-p ool=example.ntp.pool |
will configure ntp service using “example.ntp.pool” NTP pool |
ipa-client-install |
-N |
will NOT configure and NOT start a local ntp service |
ipa-client-install |
will use ntp service installed in the system and configuration when autodiscovery for _ntp._udp record |
|
ipa-client-install |
–ntp -server=1.ntp.server –ntp -server=2.ntp.server |
will configure ntp service using 1.ntp.server and 2.ntp.server NTP servers |
ipa-client-install |
–ntp-p ool=example.ntp.pool |
will configure ntp service using “example.ntp.pool” NTP pool |
Upgrade#
There are no additional actions required once the FreeIPA is upgraded.
Test Plan#
As the creation of the ntp classes is performed via the abstraction, and the specific ntp classes just redefine some of the parent class variables, it is sufficient to check the work of the abstraction based on one of the ntp services, for example:
a fresh install with the chrony service installed in the system without the “-N” option.
It is also possible to check whether the ntp service settings are fully ignored:
a fresh install with the “-N” option.
